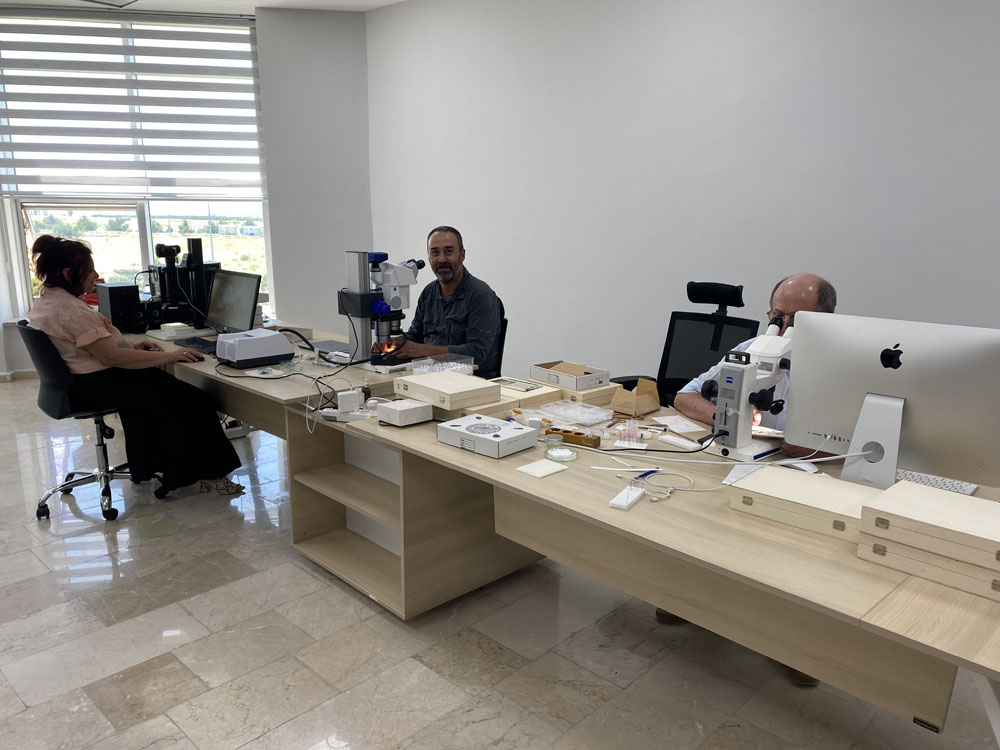
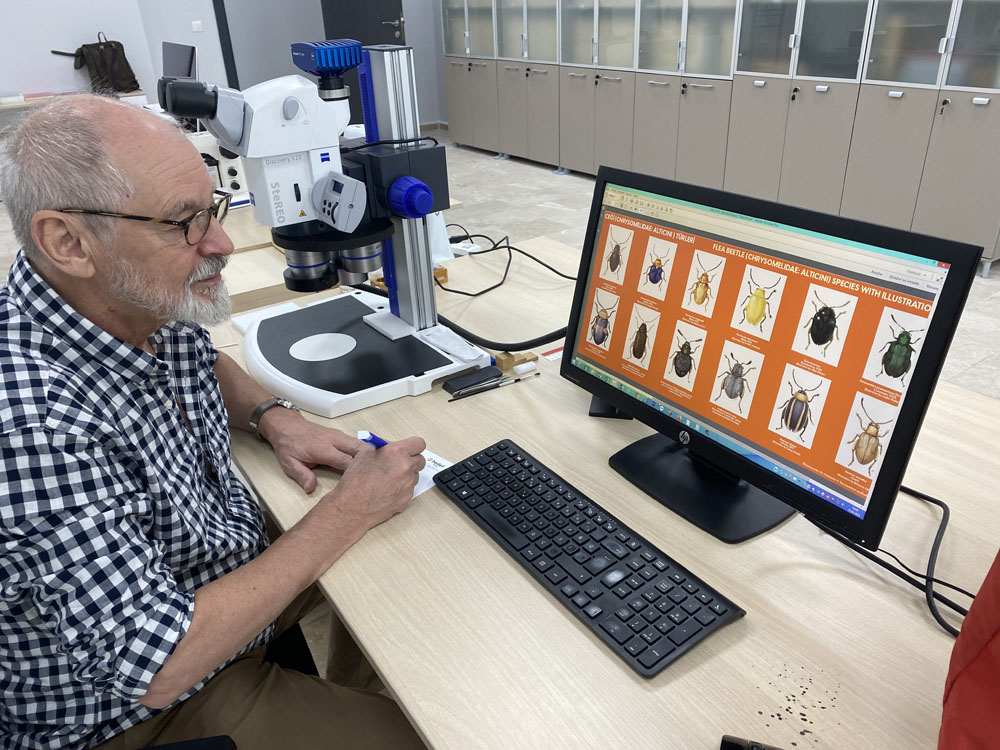
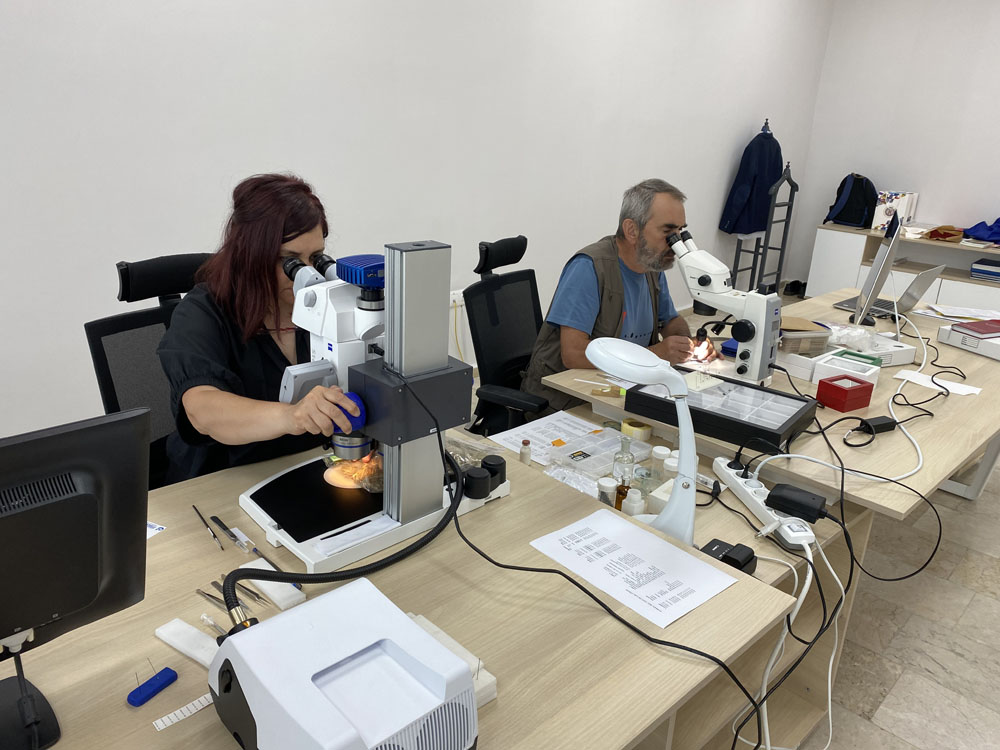
Taxonomic Research
“Taxonomic studies” refers to the systematic study and classification of living organisms based on common characteristics, evolutionary relationships, and genetic information. Taxonomy is a branch of science that aims to organize and classify the diversity of life on Earth.
The most important aspects of taxonomic research are:

Identifying Species: Taxonomists work to identify, describe and name new and existing species. This involves detailed study of morphological traits, behavior and increasingly genetic information.

Classification: The organization of living organisms into hierarchical categories such as kingdoms, phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species. This hierarchical system reflects evolutionary relationships between organisms.

Nomenclature: Assigning scientific names to organisms based on international rules (such as the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature or the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants).

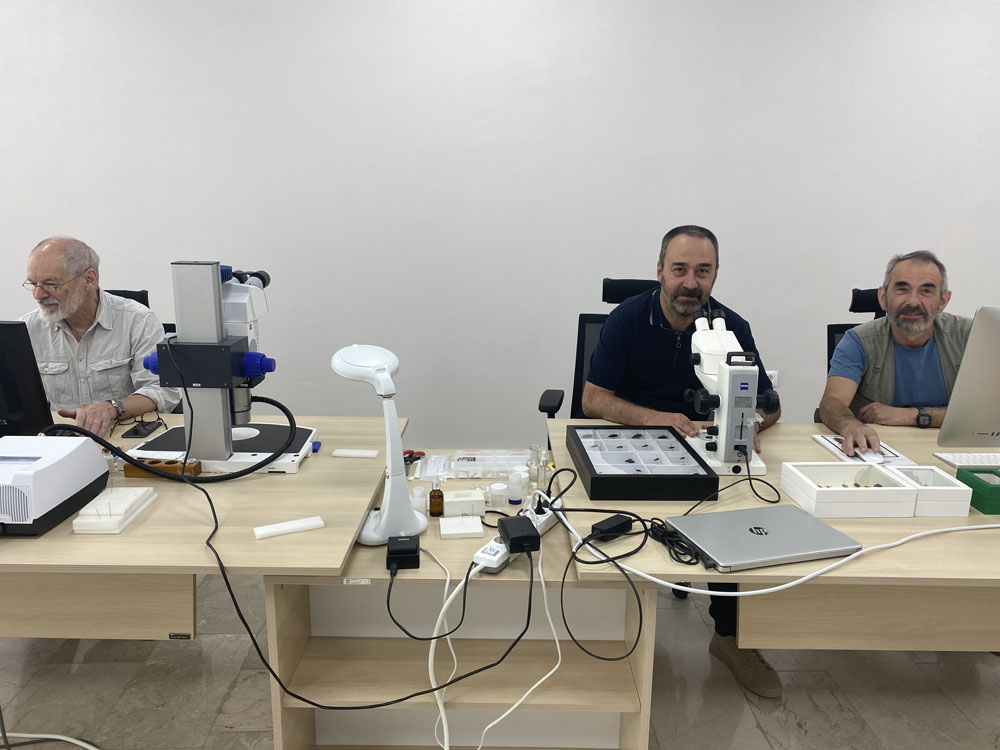
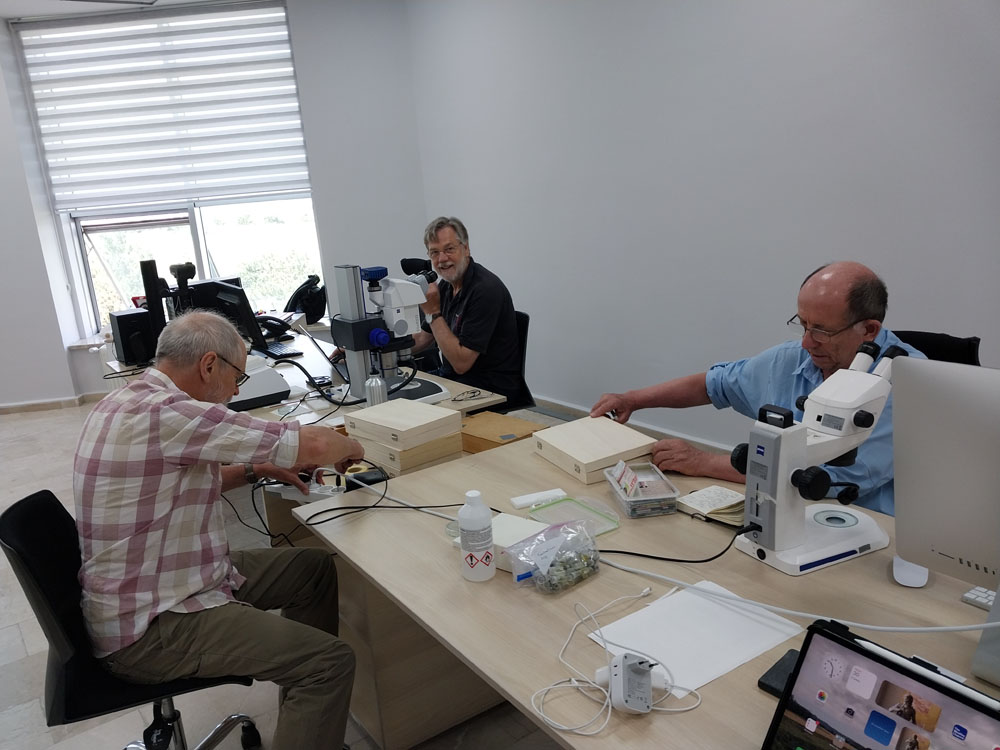
Morphological Studies: Analyzing the physical properties of organisms, including their anatomy, physiology, and other observable characteristics. This involves the use of various tools such as microscopes and imaging techniques.

Molecular Taxonomy: Combining molecular data such as DNA sequences to understand evolutionary relationships. Molecular techniques have become increasingly important in improving taxonomic classifications and resolving relationships between closely related species.

Phylogenetics: Investigation of evolutionary history and relationships between different groups of organisms. Phylogenetic trees are often constructed to visually represent the branching patterns of evolutionary lineages.

Herbarium and Museum Studies: It involves examining specimens preserved in herbariums or museums to gather information for taxonomic studies.
Type Examples: The identification and preservation of a specimen that will serve as a reference point for a species. This is crucial to ensure consistency in identifying species.

Taxonomic Keys: Developing identification tools, such as binary keys, to help others identify organisms by specific characteristics.
Cryptic Species: Identification of species that appear morphologically similar but are genetically different. Molecular techniques are often used to reveal hidden biodiversity.












